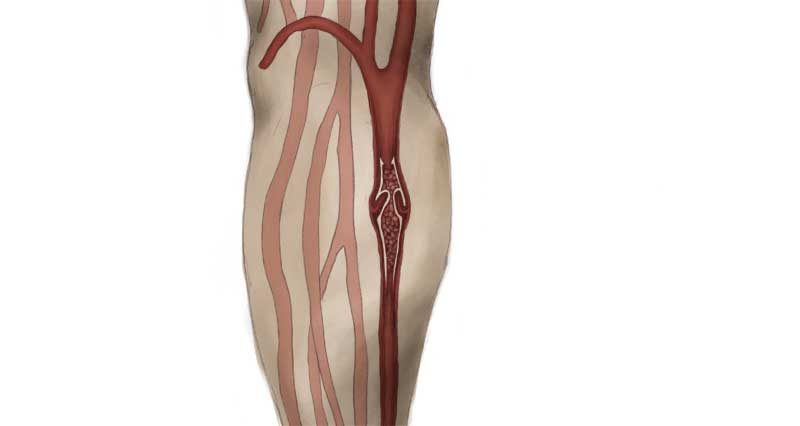
Deep Vein Thrombosis or DVT is a blood clot in a vein. It is most common in the calf muscle area, particularly following surgery and long-haul flights. Do not confuse this with a calf strain. Incorrect treatment can cause life-threatening complications.
DVT symptoms
Deep vein thrombosis symptoms consist of:
- Constant pain, usually in the calf muscle at the back of the lower leg.
- Tenderness deep within the muscle.
- You may have swelling in the calf muscle area.
- Skin temperature may seem hot to the touch.
- Sometimes a red area is visible on the skin.
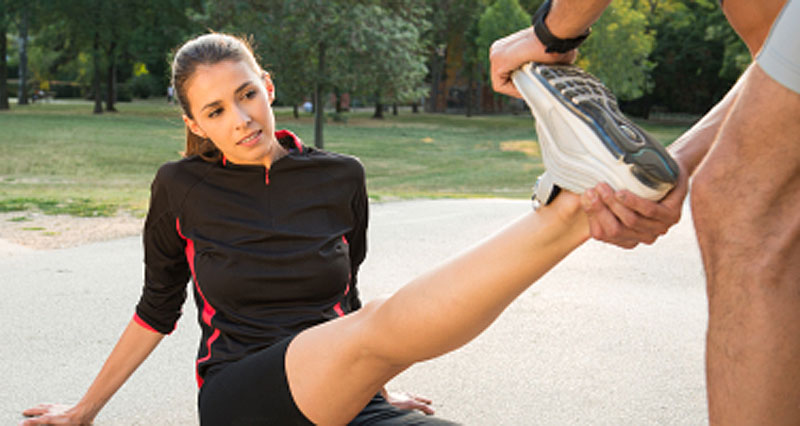
Pain may be reproduced when passively stretching the calf muscle (you relax the muscle while someone else moves your foot to stretch it.
Diagnosis
Wells’ clinical prediction rule is believed to be the best test for the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis2. It is a checklist of risk factors thought to increase risk. If the patient has more than one out of a potential nine then a DVT is likely.
What is Deep vein thrombosis?
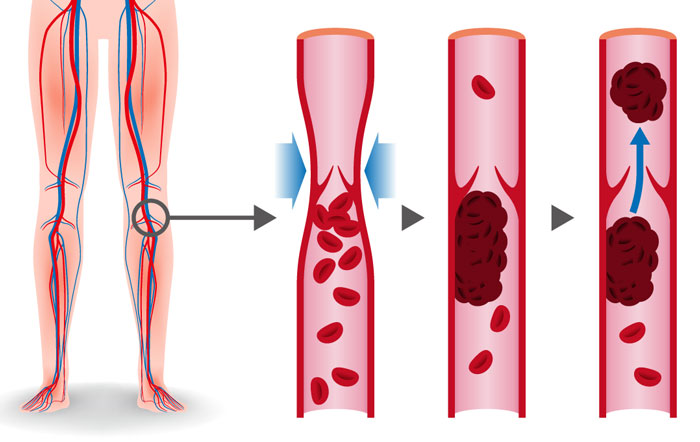
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in a vein. It is most common in the calf muscle area, particularly following surgery, or in those who have had long-haul flights. This is because the patient has been sitting still for long periods, combined with a change in air pressure. It may also develop as a complication of arthroscopic surgery1.
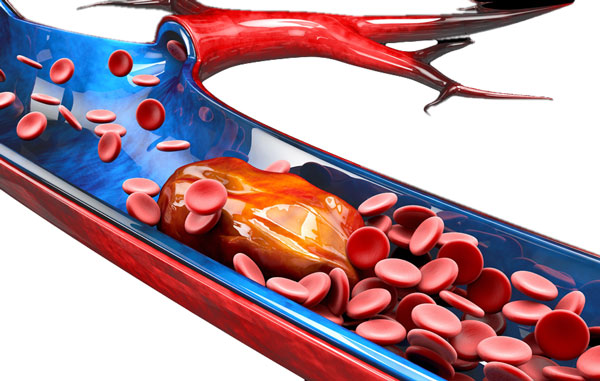
DVT is relatively common, especially in the following:
- Overweight people
- Those over the age of 50
- People who have poor circulation.
It is not something you would expect in young fit athletes. However, the condition is potentially fatal if not recognised. This is because if the blood clot breaks loose it may make its way up the circulatory system to the heart, lungs, or brain. As a result, potentially causes a heart attack, pulmonary embolism, or stroke.
If a massage therapist misses this or misdiagnoses a DVT as a calf strain and applies deep tissue massage to the area then this could work the clot free and cause serious harm or worse.
Treatment
If you suspect a DVT then seek medical attention immediately. See a doctor who can give a professional opinion and refer you for further investigations. A scan will confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment usually involves daily injections of an anticoagulant known as Heparin for up to a week.
This is followed by a second anticoagulant medication called Warfarin, taken in pill form, on a daily basis for up to 6 months.
Your doctor will do regular blood tests to ensure the medication dose is correct. Too much Warfarin increases the risk of bleeding and too little increases the risk of the clot growing.
Important! – Warfarin should not be used in patients who are pregnant as it can cause birth defects.
References
- Jaureguito JW, Greenwald AE, Wilcox JF et al. The incidence of deep venous thrombosis after arthroscopic knee surgery. Am J Sports Med 1999;27(6):707–10.
- Wells PS, Hirsh J, Anderson DR et al. Accuracy of clinical assessment of deep-vein thrombosis. Lancet, 1995;345(8961):1326-30.